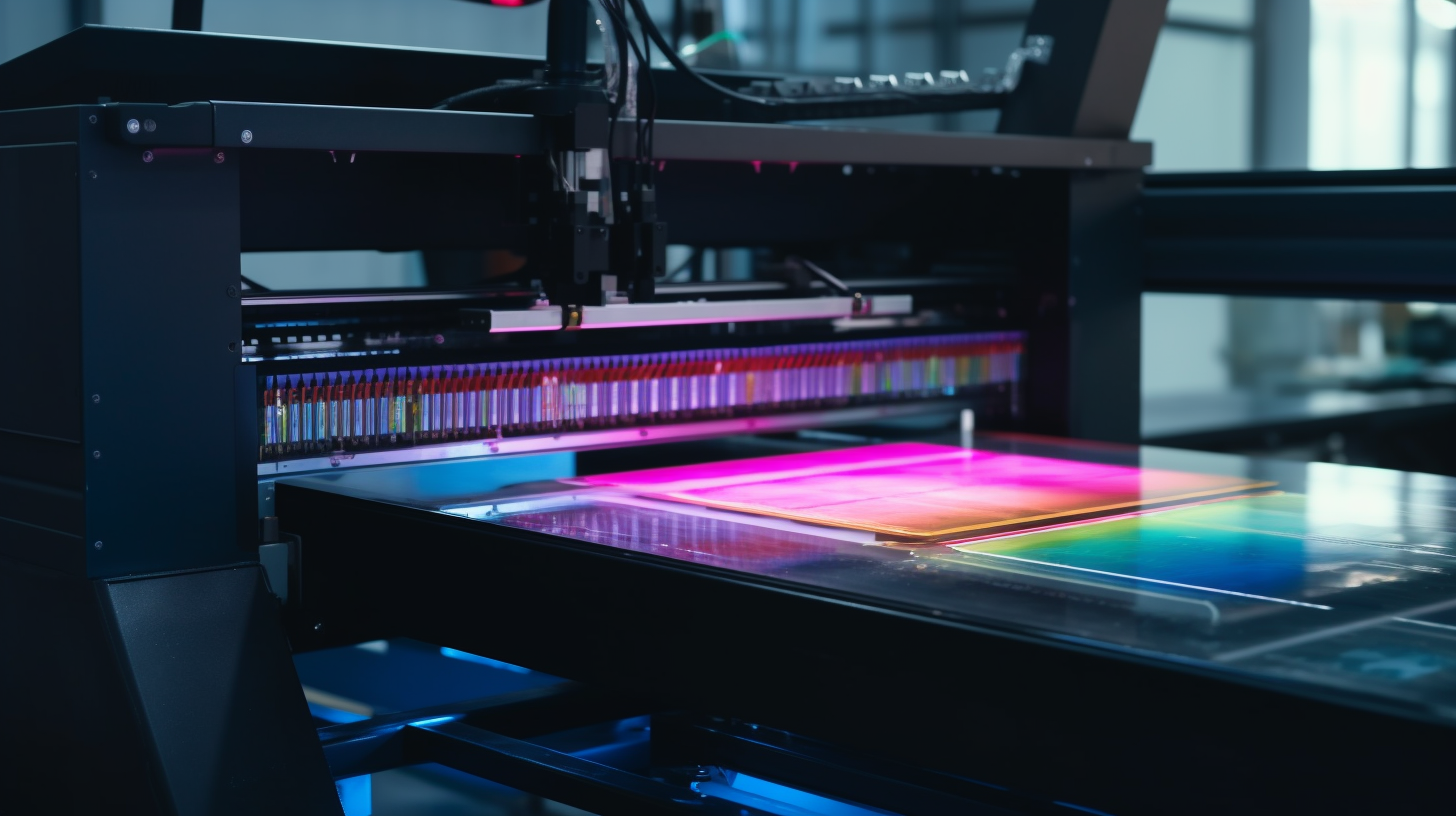
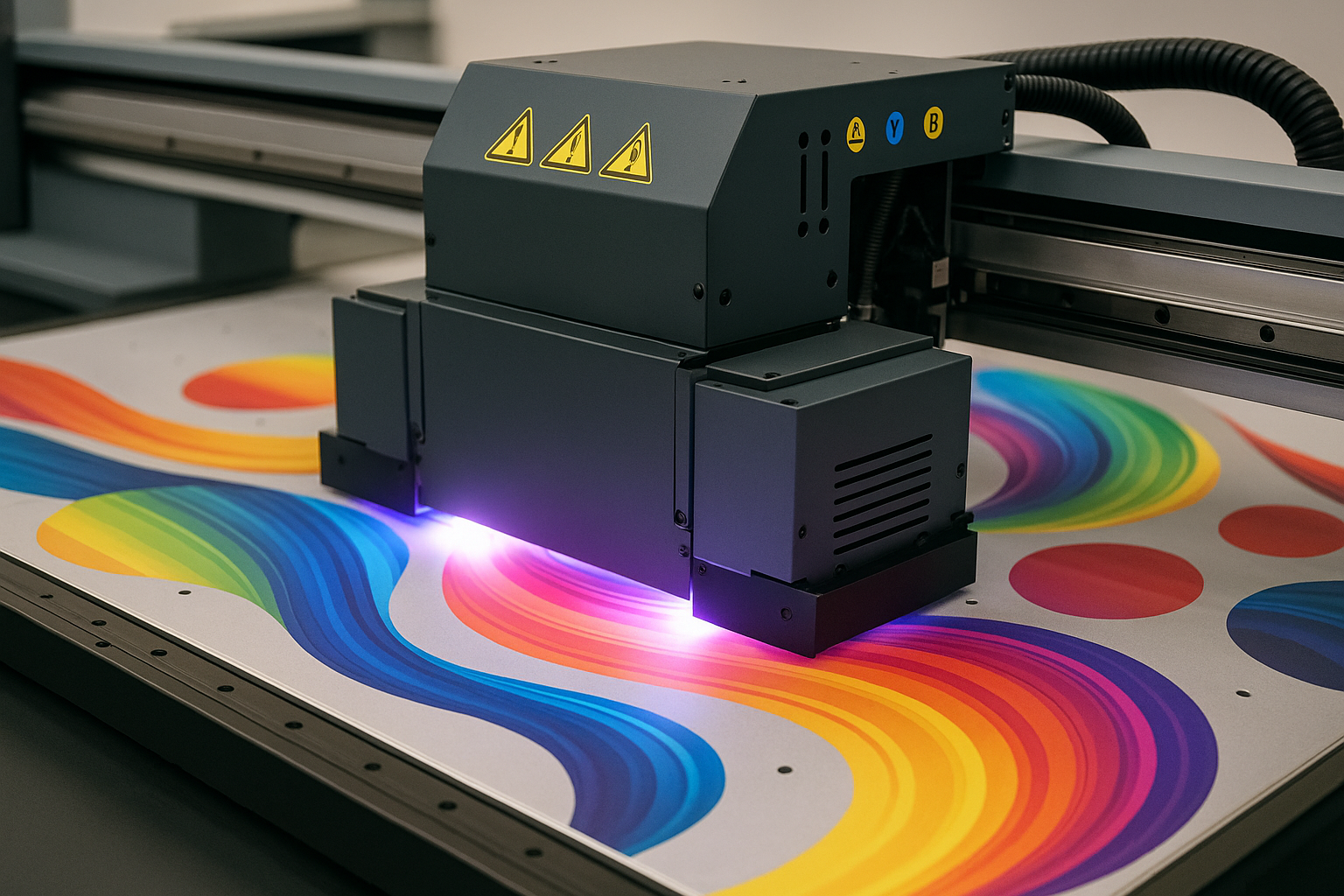
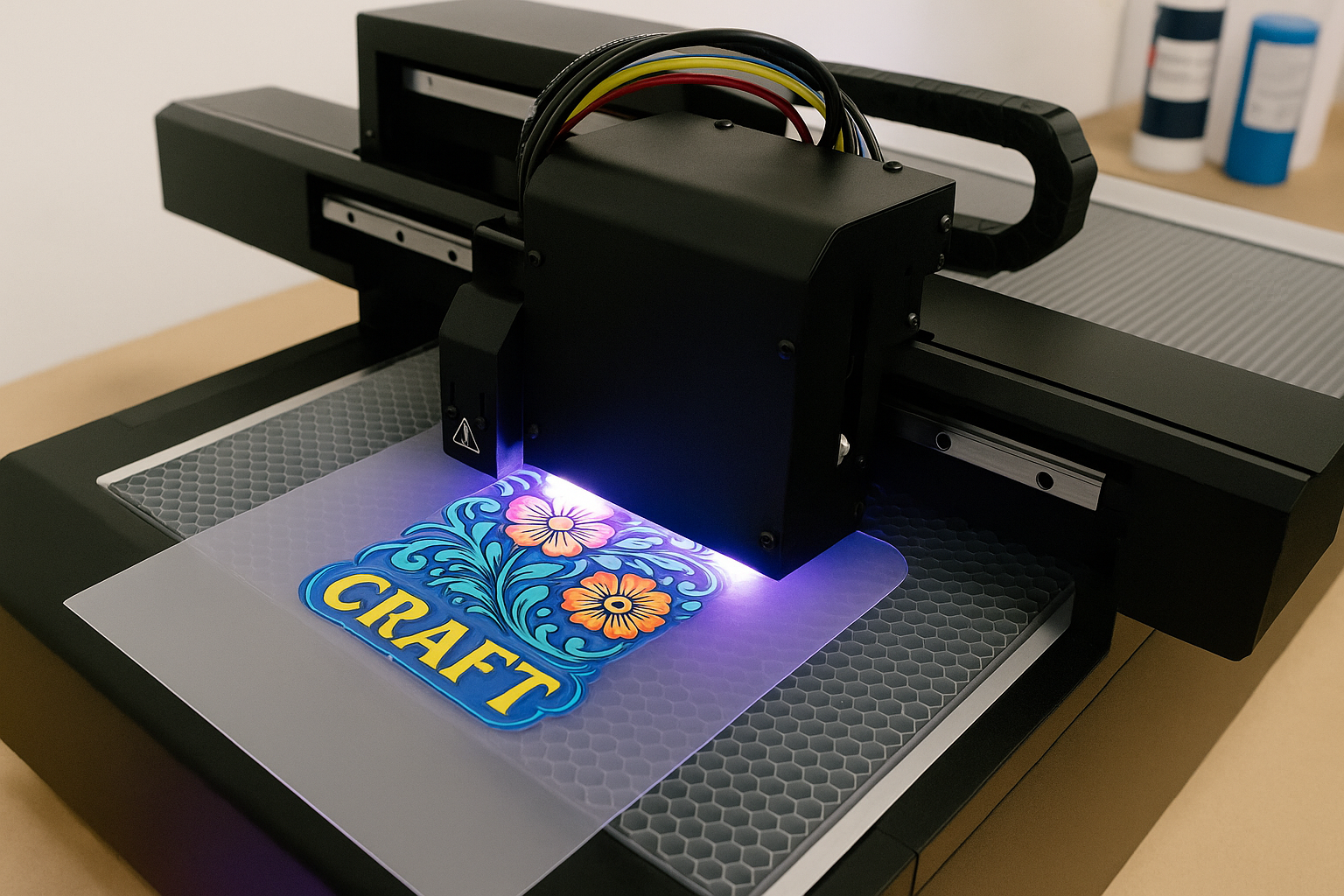
Executive Summary
UV inkjet printers have emerged as a game-changing technology in the industrial printing landscape, offering unprecedented versatility in
printing on rigid substrates and flexible materials alike. Through advanced
UV curing technology, these systems deliver exceptional print quality, durability, and production efficiency that traditional printing methods simply cannot match. This comprehensive analysis explores the technical foundations, competitive advantages, and real-world applications that make UV inkjet printing the preferred choice for businesses seeking to modernize their production capabilities and expand market opportunities.
For B2B decision-makers evaluating printing technology investments, understanding UV inkjet capabilities is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that drive long-term operational success and competitive advantage.
Introduction
The printing industry has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past two decades, with digital technologies gradually displacing traditional analog methods across numerous applications. Among these innovations,
UV inkjet printers stand out as particularly revolutionary, fundamentally changing how businesses approach production printing challenges.
Unlike conventional printing technologies that rely on solvent evaporation or absorption for ink drying, UV inkjet systems utilize ultraviolet light to instantly cure specially formulated inks through photopolymerization. This process enables immediate handling of printed materials while delivering superior adhesion, durability, and color vibrancy across an extensive range of substrates.
The significance of this technology extends far beyond simple process improvements.
UV curing capabilities have opened entirely new market segments for printing service providers, enabling applications that were previously impossible or economically unfeasible. From packaging and signage to industrial marking and decorative applications, UV inkjet printing has become an essential tool for businesses seeking operational flexibility and market differentiation.
As manufacturing trends continue emphasizing customization, shorter run lengths, and faster turnaround times, UV inkjet technology provides the operational agility needed to remain competitive in rapidly evolving markets. This analysis will examine the technical foundations that make this possible and explore specific applications where UV inkjet printing delivers measurable business advantages.
Understanding UV Inkjet Printing Technology
Core Technology Principles
UV inkjet printers operate on fundamentally different principles compared to traditional solvent-based or aqueous inkjet systems. The technology centers around specially formulated UV-curable inks that remain liquid until exposed to specific wavelengths of ultraviolet light, at which point they undergo rapid polymerization to form a solid, durable printed layer.
The printing process begins with precision inkjet heads depositing UV ink onto the substrate surface in controlled patterns determined by digital design files. Immediately following ink deposition, integrated UV LED arrays or mercury vapor lamps expose the printed areas to concentrated ultraviolet energy. This exposure triggers photopolymerization reactions within the ink chemistry, causing liquid ink to transform into a solid, cross-linked polymer film within seconds.
This instant curing mechanism provides several critical advantages over conventional drying methods. Since no solvents require evaporation and no absorption into porous substrates is necessary, printed materials can be immediately handled, stacked, or processed further without risk of smearing or quality degradation. Additionally, the polymerization process creates exceptionally strong adhesion bonds between the cured ink and substrate surface, resulting in superior durability characteristics.
UV Curing Chemistry and Process Control
The effectiveness of
UV curing depends on precise control of several interconnected variables, including lamp intensity, exposure duration, ink formulation chemistry, and substrate characteristics. Modern UV inkjet systems incorporate sophisticated monitoring and control systems that automatically adjust these parameters to optimize curing performance across different materials and printing conditions.
Photoinitiator Technology: UV-curable inks contain specialized photoinitiator compounds that absorb UV energy and generate free radicals, which initiate the polymerization reaction. Different photoinitiator systems are optimized for specific wavelength ranges, allowing ink formulations to be tailored for particular UV lamp technologies and curing requirements.
Cross-Linking Density: The degree of cross-linking achieved during curing directly impacts final print durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance. Advanced UV ink formulations balance cross-linking density to provide optimal performance characteristics for specific application requirements.
Substrate Interaction: Unlike traditional inks that rely primarily on absorption or mechanical adhesion, UV-cured inks form chemical bonds with many substrate materials, creating superior adhesion strength and durability. This characteristic enables successful
printing on rigid substrates that would be problematic for conventional printing technologies.
Equipment Architecture and Key Components
Modern
UV inkjet printers integrate several sophisticated subsystems that work together to deliver consistent, high-quality output across diverse applications and materials.
Printhead Technology: Industrial UV inkjet systems typically employ piezoelectric or thermal inkjet printheads specifically designed for UV ink compatibility. These printheads must resist UV ink chemistry effects while maintaining consistent drop formation and placement accuracy over extended operating periods.
UV Curing Modules: UV curing systems vary significantly in design and technology, ranging from traditional mercury vapor lamps to modern LED-based arrays. LED UV systems offer numerous advantages including instant on/off capability, reduced heat generation, longer service life, and more precise wavelength control.
Substrate Handling Systems: The ability to process diverse substrate types and sizes represents a key advantage of UV inkjet technology. Advanced substrate handling systems accommodate materials ranging from thin flexible films to thick rigid panels, enabling
printing on rigid substrates up to several inches thick.
Environmental Controls: UV printing systems require precise environmental control to maintain consistent ink viscosity, substrate positioning, and curing performance. Integrated temperature and humidity monitoring systems ensure optimal operating conditions regardless of external environmental variations.
Key Advantages of UV Inkjet Printing Technology
Superior Substrate Versatility
One of the most compelling advantages of
UV inkjet printers lies in their exceptional substrate compatibility. Traditional printing methods often require specific substrate treatments, coatings, or material properties to achieve acceptable results. UV inkjet technology eliminates many of these limitations through its unique curing mechanism and advanced ink chemistry.
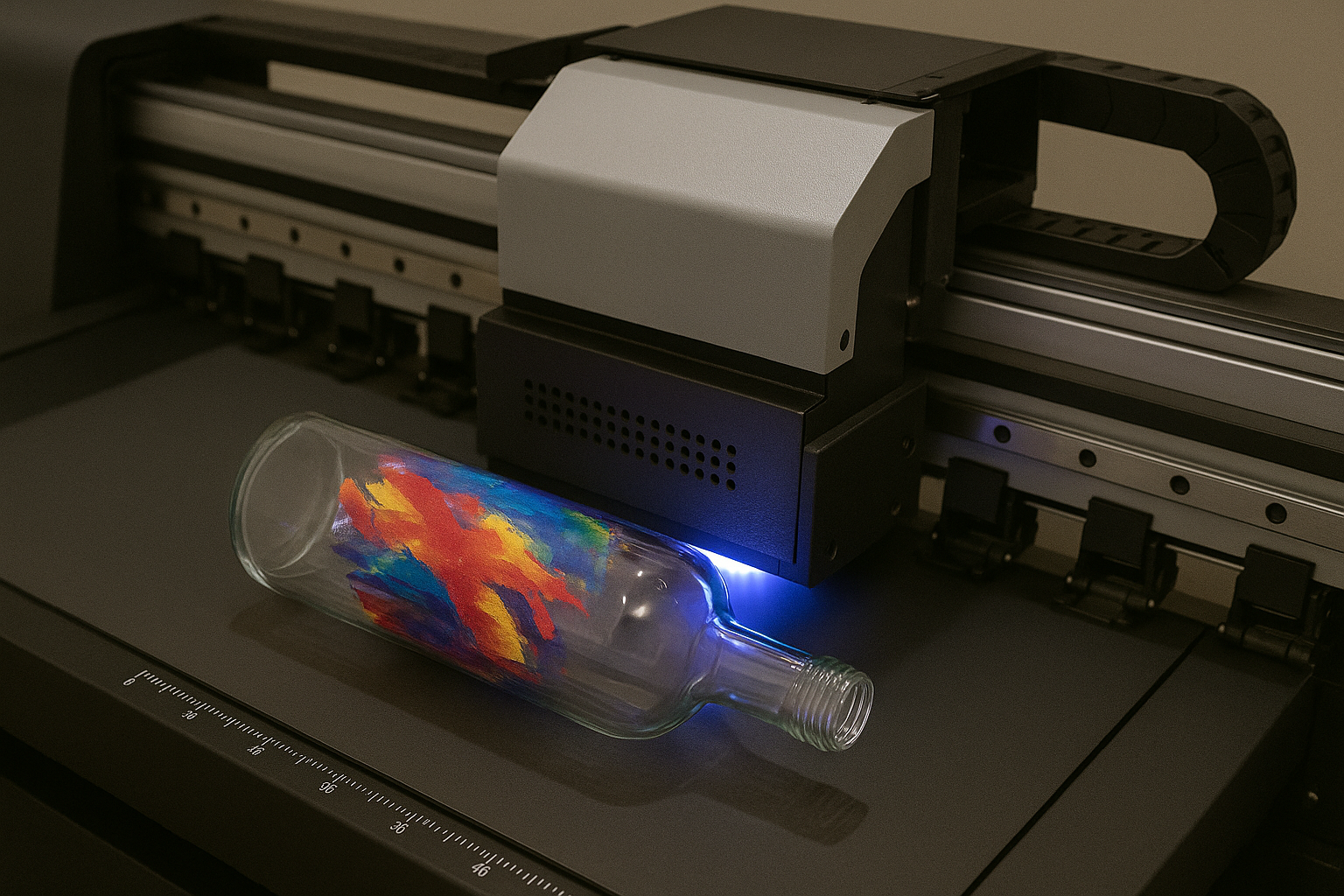
Rigid Substrate Capabilities: Printing on rigid substrates represents a particular strength of UV inkjet technology. Materials such as acrylic, aluminum, wood, glass, ceramic, and various composite materials can be printed directly without pretreatment or special preparation. This capability opens numerous application opportunities in signage, industrial manufacturing, architectural applications, and specialty product decoration.
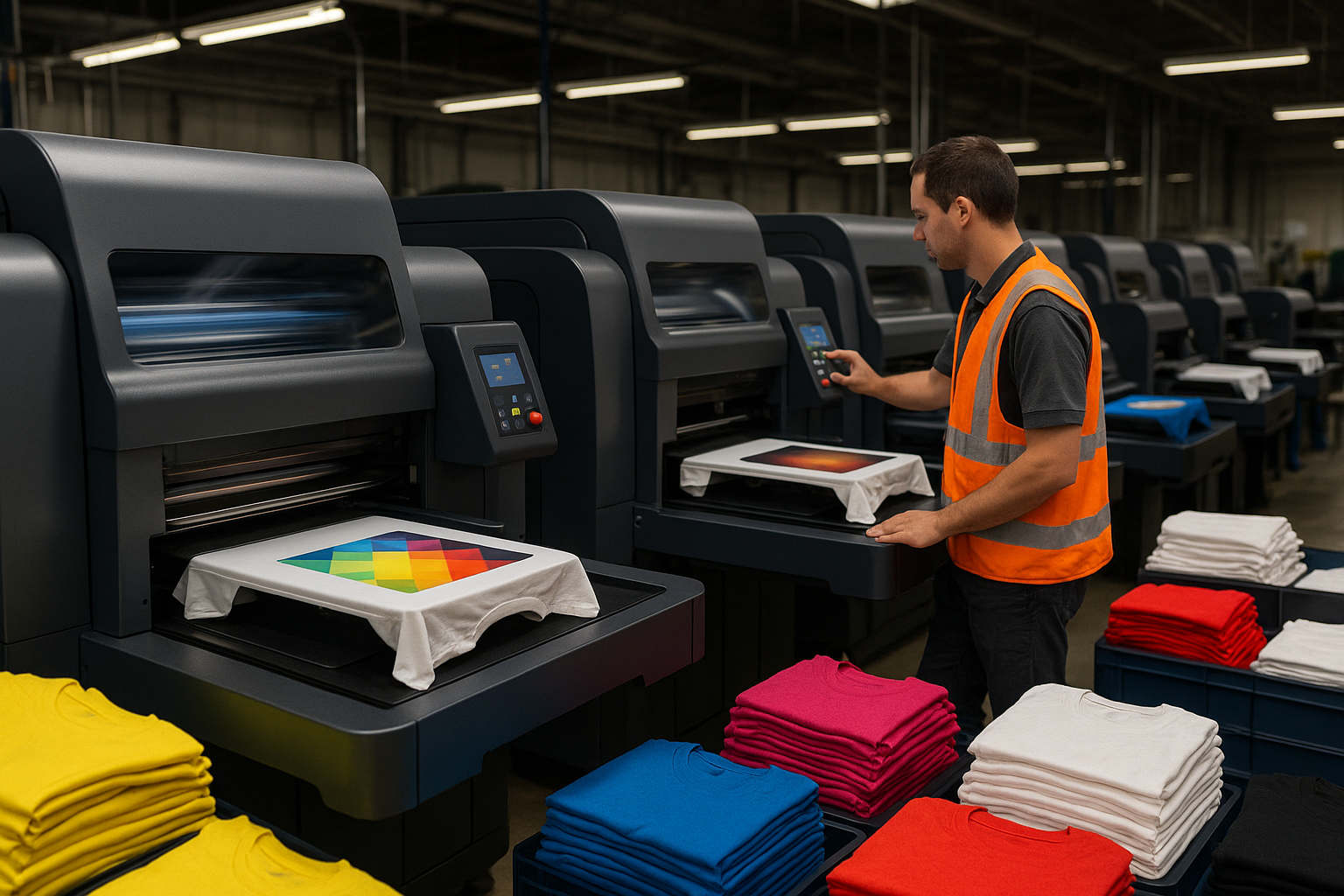
Flexible Material Processing: Despite the focus on rigid materials, UV inkjet systems also excel at printing flexible substrates including films, fabrics, vinyl, and paper products. The instant curing characteristic prevents ink migration or bleeding that can compromise print quality on porous or absorbent materials.
Thickness Accommodation: Modern UV inkjet systems can accommodate substrate thicknesses ranging from thin films measured in microns to rigid panels several centimeters thick. This versatility enables diverse applications from packaging labels to architectural panels using a single printing platform.
Enhanced Durability and Performance
UV curing technology produces printed graphics with exceptional durability characteristics that often exceed the performance of traditional printing methods by significant margins.
Weather Resistance: UV-cured inks demonstrate superior resistance to UV degradation, moisture, temperature extremes, and atmospheric pollutants. This characteristic makes UV inkjet printing ideal for outdoor applications including signage, vehicle graphics, and architectural elements.
Chemical Resistance: The cross-linked polymer structure created during
UV curing provides excellent resistance to solvents, cleaning chemicals, and industrial fluids. This property is particularly valuable for industrial labeling, chemical packaging, and automotive applications.
Mechanical Durability: UV-cured prints resist scratching, abrasion, and impact damage significantly better than conventional printed materials. The hard, polymerized surface maintains appearance and functionality even under demanding use conditions.
Adhesion Strength: The chemical bonding that occurs between UV-cured inks and many substrate materials creates adhesion strength that often exceeds the cohesive strength of the substrate itself. This characteristic eliminates common failure modes associated with traditional printing methods.
Production Efficiency and Economic Benefits
UV inkjet printers offer numerous operational advantages that translate directly into improved production efficiency and economic performance.
Instant Handling: The immediate curing provided by
UV curing eliminates drying time requirements, enabling printed materials to be immediately processed, stacked, or shipped. This characteristic significantly reduces production cycle times and workspace requirements.
Reduced Waste: The precision of digital inkjet technology combined with instant curing minimizes material waste compared to traditional printing methods. Setup waste is virtually eliminated, and job changeovers require no cleanup or preparation time.
Variable Data Capability: UV inkjet systems excel at variable data printing applications where each printed piece contains unique information. This capability supports mass customization, serialization, and personalization applications that add significant value to printed products.
Energy Efficiency: Modern LED UV curing systems consume significantly less energy than traditional curing methods while generating minimal heat. This efficiency reduces operating costs and improves working conditions in production environments.
Industrial Applications and Market Opportunities
Packaging and Label Printing
The packaging industry has embraced
UV inkjet printers for their ability to produce high-quality graphics on diverse packaging materials while meeting demanding production requirements.
Flexible Packaging Applications: UV inkjet technology enables direct printing on flexible packaging films, eliminating the need for pre-printed materials and reducing inventory requirements. The instant curing characteristic prevents ink penetration that could compromise package integrity or food safety.
Rigid Packaging Solutions: Printing on rigid substrates such as folding cartons, plastic containers, and glass packaging provides brands with enhanced decoration capabilities and supply chain efficiency. UV inkjet systems can print directly onto formed packages, enabling late-stage customization and reducing packaging inventory complexity.
Industrial Labeling: The durability characteristics of
UV curing technology make it ideal for industrial labels that must withstand harsh environmental conditions, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. Applications include chemical containers, automotive components, and electronic equipment labeling.
Signage and Display Graphics
The signage industry represents one of the largest markets for
UV inkjet printers, driven by the technology’s versatility and durability advantages.
Outdoor Signage Applications: UV-cured graphics demonstrate exceptional longevity in outdoor environments, maintaining color accuracy and physical integrity for years without protective laminates. This durability reduces maintenance costs and extends replacement intervals for outdoor signage installations.
Architectural Graphics: Printing on rigid substrates enables creation of architectural elements including wall panels, decorative screens, and interior design elements. The ability to print directly onto construction materials streamlines installation processes and reduces material costs.
Point-of-Purchase Displays: The rapid turnaround capability of UV inkjet printing supports dynamic point-of-purchase campaigns where graphics must be updated frequently to match promotional cycles and inventory changes.
Industrial Manufacturing and Product Decoration
UV inkjet printers have found extensive application in industrial manufacturing processes where traditional decoration methods are impractical or economically unfeasible.
Electronic Component Marking: The precision and durability of UV inkjet printing make it ideal for marking electronic components, circuit boards, and assemblies with tracking codes, specifications, and branding information.
Automotive Applications: UV inkjet technology supports automotive interior and exterior decoration applications where durability, chemical resistance, and precise color matching are critical requirements.
Medical Device Labeling: The biocompatibility of properly formulated UV-cured inks, combined with excellent durability characteristics, makes UV inkjet printing suitable for medical device labeling and marking applications.
Specialty and Emerging Applications
The versatility of
UV inkjet printers continues to enable new applications as technology advances and market requirements evolve.
Textile and Apparel: UV inkjet printing on synthetic fabrics and leather goods provides decoration options that traditional textile printing methods cannot achieve, particularly for technical fabrics and performance materials.
Glass and Ceramic Decoration: The ability to print directly onto glass and ceramic surfaces without pretreatment enables new product decoration possibilities in architectural, automotive, and consumer product applications.
3D Object Printing: Advanced UV inkjet systems can print on curved and irregular surfaces, enabling decoration of three-dimensional objects that would be impossible to process with traditional printing methods.
Technology Selection and Implementation Considerations
Equipment Evaluation Criteria
Selecting appropriate
UV inkjet printers requires careful evaluation of numerous technical and operational factors that impact long-term success and return on investment.
Production Volume Requirements: UV inkjet systems are available in configurations ranging from desktop units suitable for prototyping to industrial-scale platforms capable of continuous production. Matching equipment capacity to production requirements ensures optimal utilization and economic performance.
Substrate Compatibility: While UV inkjet technology offers broad substrate compatibility, specific ink formulations and curing systems may be optimized for particular material types. Understanding intended applications enables selection of systems with optimal performance characteristics.
Print Quality Specifications: Different UV inkjet systems offer varying resolution capabilities, color gamut, and print quality characteristics. Applications requiring photographic quality demand different equipment specifications than those focused on industrial marking or packaging.
Environmental Requirements: UV inkjet systems require controlled environmental conditions for optimal performance. Facility planning must accommodate ventilation, temperature control, and safety requirements associated with UV curing equipment.
Implementation Planning and Best Practices
Successful UV inkjet implementation requires comprehensive planning that addresses technical, operational, and business requirements.
Workflow Integration: UV inkjet systems must integrate effectively with existing production workflows and business systems. Digital workflow software, color management systems, and production scheduling tools require careful evaluation and implementation.
Operator Training: While UV inkjet systems are generally more user-friendly than traditional printing equipment, proper operator training ensures optimal performance and prevents costly mistakes or equipment damage.
Maintenance Planning: Preventive maintenance programs are essential for maintaining UV inkjet system performance and reliability. Understanding maintenance requirements and costs enables accurate total cost of ownership calculations.
Safety Considerations: UV curing systems require appropriate safety measures to protect operators from UV exposure and ensure compliance with occupational safety regulations.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Technology Evolution and Advancement
UV inkjet printers continue to evolve rapidly, with ongoing developments in ink chemistry, curing technology, and system integration driving expanded capabilities and applications.
LED UV Technology: The transition from traditional mercury vapor lamps to LED UV curing systems represents a significant technological advancement, offering improved efficiency, longer service life, and enhanced process control capabilities.
Advanced Ink Formulations: Ongoing development of specialized UV-curable inks enables new applications and improved performance characteristics. Recent advances include low-migration inks for food packaging, flexible inks for textile applications, and conductive inks for electronic applications.
System Integration: Modern UV inkjet systems increasingly integrate with digital workflow systems, automated material handling equipment, and quality control systems to create comprehensive production solutions.
Market Growth Drivers
Several factors continue to drive growth in the
UV inkjet printers market, creating opportunities for both equipment manufacturers and end users.
Customization Demand: Increasing consumer and business demand for customized products drives adoption of digital printing technologies that can economically produce short runs and variable content.
Sustainability Requirements: UV curing technology offers environmental advantages compared to solvent-based printing methods, including reduced volatile organic compound emissions and elimination of solvent disposal requirements.
Supply Chain Optimization: The ability to print locally and on-demand reduces inventory requirements and transportation costs while improving supply chain responsiveness.
Regulatory Compliance: Evolving regulations regarding food packaging safety, product traceability, and environmental impact favor UV inkjet technology advantages.
Investment Considerations and ROI Analysis
UV inkjet printers represent significant capital investments that require careful financial analysis to ensure positive returns and strategic alignment.
Cost Structure Analysis: Understanding the total cost of ownership for UV inkjet systems requires evaluation of equipment costs, consumables, maintenance, facility requirements, and operational expenses.
Revenue Opportunity Assessment: UV inkjet capabilities can enable new service offerings and market segments that generate additional revenue streams beyond traditional printing applications.
Competitive Positioning: UV inkjet technology can provide competitive advantages through improved quality, faster turnaround times, and expanded application capabilities that differentiate service offerings.
Technology Lifecycle Planning: Rapid advancement in UV inkjet technology requires consideration of upgrade paths and technology obsolescence risks when making equipment investments.
Conclusion
UV inkjet printers represent a transformative technology that has fundamentally changed the landscape of industrial printing applications. Through the combination of digital precision, instant
UV curing, and exceptional substrate versatility, these systems enable applications and capabilities that were previously impossible or economically unfeasible.
The ability to achieve high-quality
printing on rigid substrates while maintaining production efficiency and durability standards makes UV inkjet technology an essential tool for businesses seeking to expand their market opportunities and operational capabilities. From packaging and signage to industrial manufacturing and specialty applications, UV inkjet printing continues to enable innovation and growth across diverse market segments.
For B2B decision-makers evaluating printing technology investments, UV inkjet systems offer compelling advantages in operational flexibility, production efficiency, and market positioning. The combination of immediate handling capabilities, superior durability, and broad substrate compatibility provides a foundation for sustainable competitive advantage in increasingly demanding markets.
As technology continues to advance and market requirements evolve,
UV inkjet printers are positioned to play an increasingly important role in modern manufacturing and production operations. Understanding these capabilities and their business implications enables informed decision-making that supports long-term success and market leadership.
The investment in UV inkjet technology represents more than simply acquiring new equipment—it opens doors to new markets, enables innovative applications, and provides the operational agility needed to succeed in rapidly changing business environments. For organizations ready to embrace the future of digital printing, UV inkjet technology provides the tools and capabilities needed to achieve these objectives.