Meta Description:
Comprehensive inkjet vs laser printer comparison for business buyers. Expert analysis of performance, costs, and applications to guide your B2B printing investment decisions.
Introduction: The Modern Business Printing Dilemma
In today’s competitive business landscape, choosing between
inkjet vs laser printing technology represents more than just a simple equipment decision—it’s a strategic investment that impacts operational efficiency, cost management, and productivity across your organization. With the global commercial printing market projected to reach $472.35 billion by 2026, business decision-makers face increasing pressure to optimize their printing infrastructure while controlling expenses.
The
printer comparison landscape has evolved significantly, with both inkjet and laser technologies advancing rapidly to meet diverse
business printing requirements. From small startups managing tight budgets to large enterprises handling massive print volumes, understanding the fundamental differences between these technologies is crucial for making informed procurement decisions.
Technology Fundamentals: How Each System Works
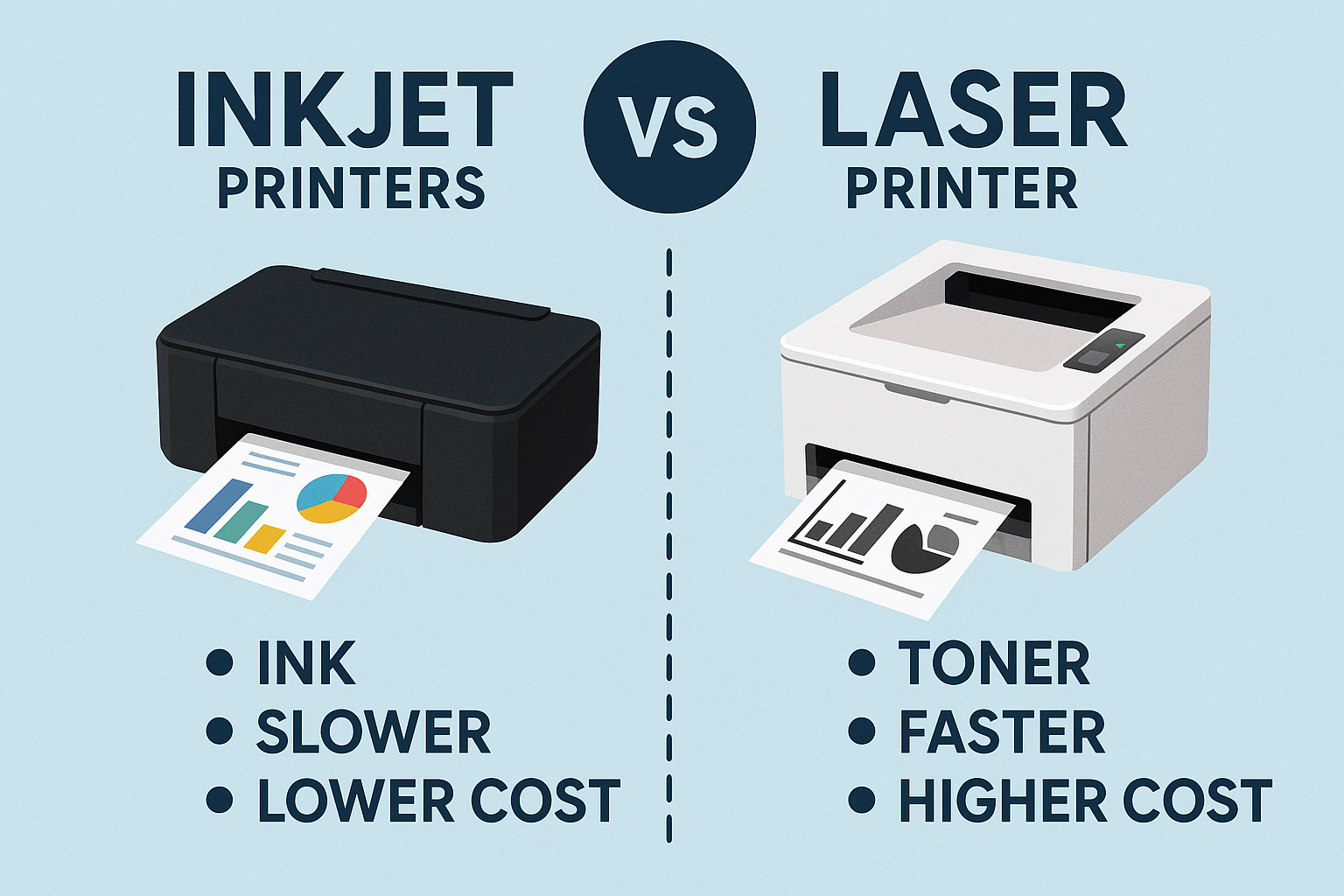
Inkjet Technology Overview
Inkjet printers operate through precision droplet deposition, where liquid ink cartridges spray microscopic droplets onto paper through heated or piezoelectric printheads. This technology excels in producing high-resolution images and graphics, with modern business inkjet systems achieving resolutions up to 4800 x 1200 dpi.
Key Technical Advantages:
- Superior color accuracy and gradation
- Excellent photo and graphic reproduction
- Versatile media compatibility
- Lower initial equipment investment
- Compact form factors for space-constrained environments
Laser Technology Framework
Laser printers utilize electrostatic printing processes, where laser beams create electrostatic images on photosensitive drums, attracting toner particles that transfer to paper through heat and pressure fusion. This
printer comparison reveals laser technology’s strength in high-volume, text-heavy applications.
Core Technical Benefits:
- Exceptional text sharpness and clarity
- Rapid printing speeds (20-100+ ppm)
- Consistent output quality over large volumes
- Superior paper handling capabilities
- Network integration and security features
Performance Analysis: Speed, Quality, and Reliability
Print Speed and Volume Capacity
When evaluating
inkjet vs laser performance for business applications, print speed becomes a critical differentiator. Laser printers typically dominate high-volume scenarios, with commercial models achieving 50-100 pages per minute, while business inkjet systems generally operate at 15-40 ppm ranges.
Volume Recommendations:
- Low Volume (< 500 pages/month): Both technologies viable
- Medium Volume (500-2,000 pages/month): Laser preferred for text, inkjet for mixed content
- High Volume (2,000+ pages/month): Laser strongly recommended
Output Quality Comparison
The
business printing quality debate centers on application requirements. Laser printers deliver unmatched text clarity with crisp, professional edges ideal for contracts, reports, and formal documentation. Conversely, inkjet technology excels in color reproduction, making it superior for marketing materials, presentations, and graphic-intensive documents.
Quality Matrix:
- Text Documents: Laser advantage (95% clarity vs 85% inkjet)
- Color Graphics: Inkjet advantage (superior color gamut)
- Mixed Content: Application-dependent choice
- Photo Printing: Inkjet clear winner
Cost Structure Analysis: Beyond Purchase Price
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Framework
Smart
printer comparison extends beyond initial acquisition costs to encompass comprehensive TCO analysis over 3-5 year operational periods. This includes equipment purchase, consumables, maintenance, and productivity factors.
TCO Components:
- Initial Investment: Equipment and setup costs
- Consumable Expenses: Ink/toner, paper, replacement parts
- Maintenance Costs: Service contracts, repairs, downtime
- Operational Factors: Energy consumption, space requirements
Consumable Cost Dynamics
The
inkjet vs laser consumable debate reveals complex cost structures. While inkjet cartridges appear expensive per unit, cost-per-page calculations often favor laser systems for high-volume applications, with laser toner typically costing
0.02−0.06perpageversus0.02-0.06 per page versus 0.02−0.06perpageversus0.04-0.15 for inkjet.
Cost Efficiency Factors:
- Page Yield: Laser toner cartridges offer 2-10x higher yields
- Print Coverage: Color inkjet costs escalate with high coverage documents
- Shelf Life: Laser toner stable for years, inkjet prone to drying
Application-Specific Recommendations
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different business sectors require tailored
business printing solutions based on unique operational requirements:
Professional Services & Legal:
- Recommendation: Laser printers
- Rationale: High-volume text documents, professional appearance, cost efficiency
Marketing & Creative Agencies:
- Recommendation: High-end inkjet systems
- Rationale: Superior color accuracy, photo quality, creative flexibility
Healthcare & Education:
- Recommendation: Hybrid approach or multifunction inkjet
- Rationale: Mixed content requirements, cost sensitivity, space constraints
Workflow Integration Assessment
Modern
printer comparison must consider workflow integration capabilities. Laser printers typically offer superior network functionality, security features, and enterprise software compatibility, while inkjet systems provide flexibility for creative workflows and mobile printing requirements.
Strategic Procurement Guidelines
Decision Matrix Framework
Implement this systematic approach for
inkjet vs laser evaluation:
- Volume Analysis: Calculate monthly/annual print requirements
- Content Assessment: Determine text-to-graphics ratio
- Budget Evaluation: Consider 3-year TCO projections
- Space Planning: Assess physical installation requirements
- Feature Matching: Align capabilities with business needs
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
Critical Selection Factors:
- Reliability Ratings: Mean time between failures (MTBF)
- Service Support: Local service availability and response times
- Consumable Availability: Global supply chain reliability
- Technology Roadmap: Future upgrade and compatibility paths
- Environmental Compliance: Energy efficiency and recycling programs
Future-Proofing Your Investment
Technology Trends Impact
The
business printing landscape continues evolving with emerging technologies including:
- Cloud Integration: Enhanced remote printing capabilities
- AI-Powered Management: Predictive maintenance and usage optimization
- Sustainability Focus: Eco-friendly consumables and energy efficiency
- Security Enhancement: Advanced encryption and access controls
Scalability Considerations
Plan for business growth by selecting systems with expansion capabilities. Laser printers typically offer better scalability for increasing volumes, while inkjet systems provide flexibility for changing content requirements.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
The
inkjet vs laser decision ultimately depends on your specific business requirements, budget constraints, and growth projections. Laser printers excel in high-volume, text-heavy environments where speed and cost-per-page efficiency matter most. Inkjet systems shine in creative applications requiring superior color quality and media versatility.
Key Decision Points:
- Choose laser for: High volumes, primarily text, cost-sensitive operations
- Choose inkjet for: Color-critical work, low volumes, space constraints, photo printing
Recommended Action Steps:
- Conduct detailed volume and content analysis
- Calculate 3-year TCO for both technologies
- Test print samples relevant to your applications
- Evaluate vendor support and service capabilities
- Consider hybrid solutions for diverse requirements
The most successful
business printing strategies often involve understanding that there’s no universal “best” choice—only the optimal solution for your specific organizational needs and operational context.